
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- What is Compatibility Testing?
- Why is Compatibility Testing Important?
- When to Perform Compatibility Testing?
- How to Perform Compatibility Testing?
- Types of Compatibility Testing
- Compatibility Test Tools
- Compatibility Testing on the Cloud
- Who is Involved in Compatibility Testing?
- Benefits of Compatibility Testing
- Challenges of Compatibility Testing
- Best Practices for Compatibility Testing
- Example of Compatibility Testing
- Is Compatibility Testing Akin to Cross Browser/Device Testing?
What is Compatibility Testing: Tutorial with Examples
In this guide to compatibility testing, learn how to build compatible software applications for different platforms and environments.
Dileep Marway
February 6, 2026
Testing compatibility is a technique to check the functionality of software applications across different web browsers and versions, mobile devices, databases, operating systems, hardware, and networks. This process ensures the software applications work correctly across all platforms and environments as intended.
The software compatibility testing market is expected to grow significantly by 2029, with a high annual growth rate of 8.3% between 2023 and 2029. In today’s digital age, the market is flooded with different types of browsers, browser versions, platforms, devices, and operating systems.
Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that websites and mobile applications are compatible across all platforms and that they provide a seamless user experience. This can be done by testing software application compatibility.
What is Compatibility Testing?
Compatibility testing checks if the software can run on different hardware, operating systems (OS), applications, network environments, or mobile devices.
It is a vital part of a QA strategy, and if this has yet to be thought of in your approach, I recommend that you do some research and make it a crucial part of your approach.
Given that there are many devices/browsers, you must have a strategic plan to ensure that compatibility tests are factored into your testing strategy. For me, compatibility tests are a form of not discriminating against devices/browsers that a particular user may use.
Why is Compatibility Testing Important?
Far too many times, I have used websites on my iPhone where I cannot buy the product I want, or I’m on my MacBook, and a website cuts off the right-hand side of the Safari browser.
I’m sure we have all been frustrated in these ways before, and it is an annoyance that hinders the user flow. As a customer, I’m willing to spend more on a product if the website user experience aids the user flow.
If we look at the mobile device market, it is highly fragmented. This can be seen in the stats below:
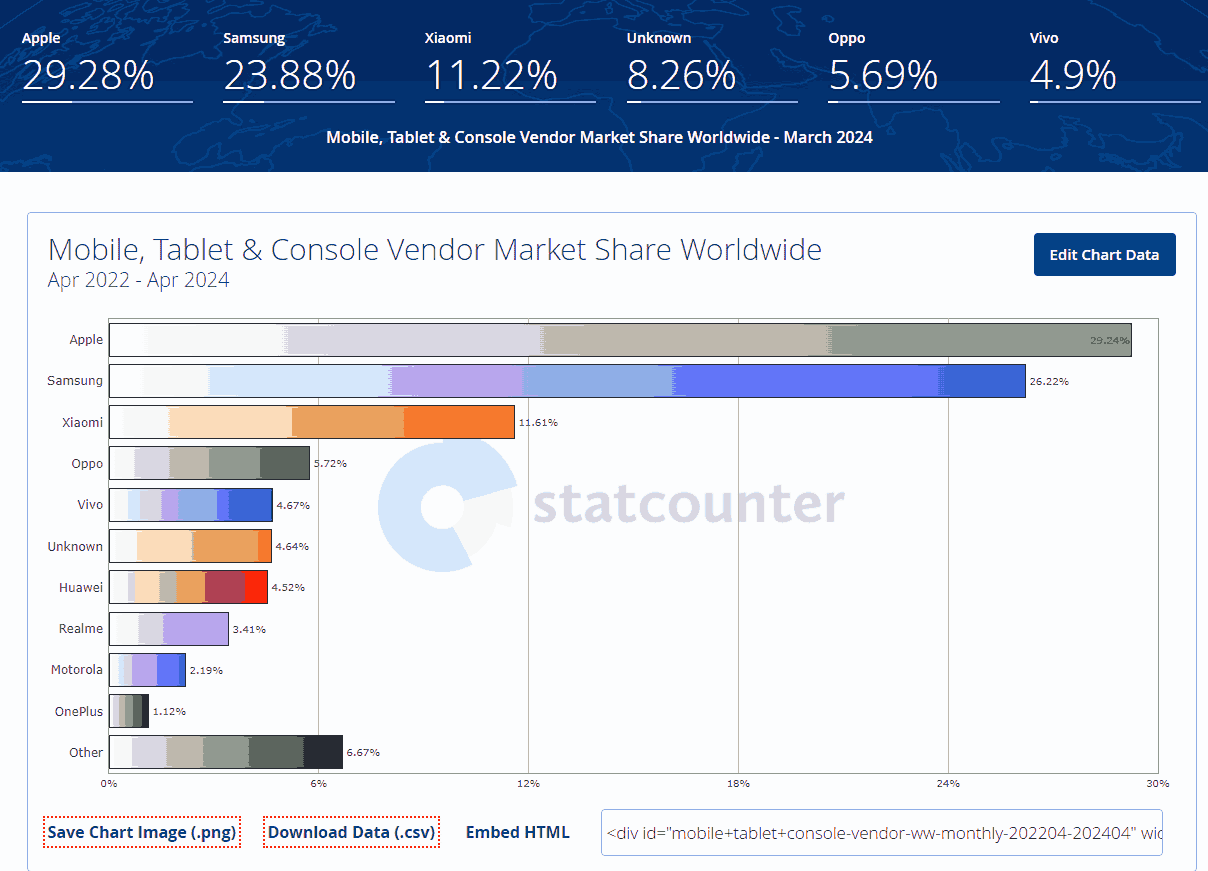
The same goes for the web browser market as well.
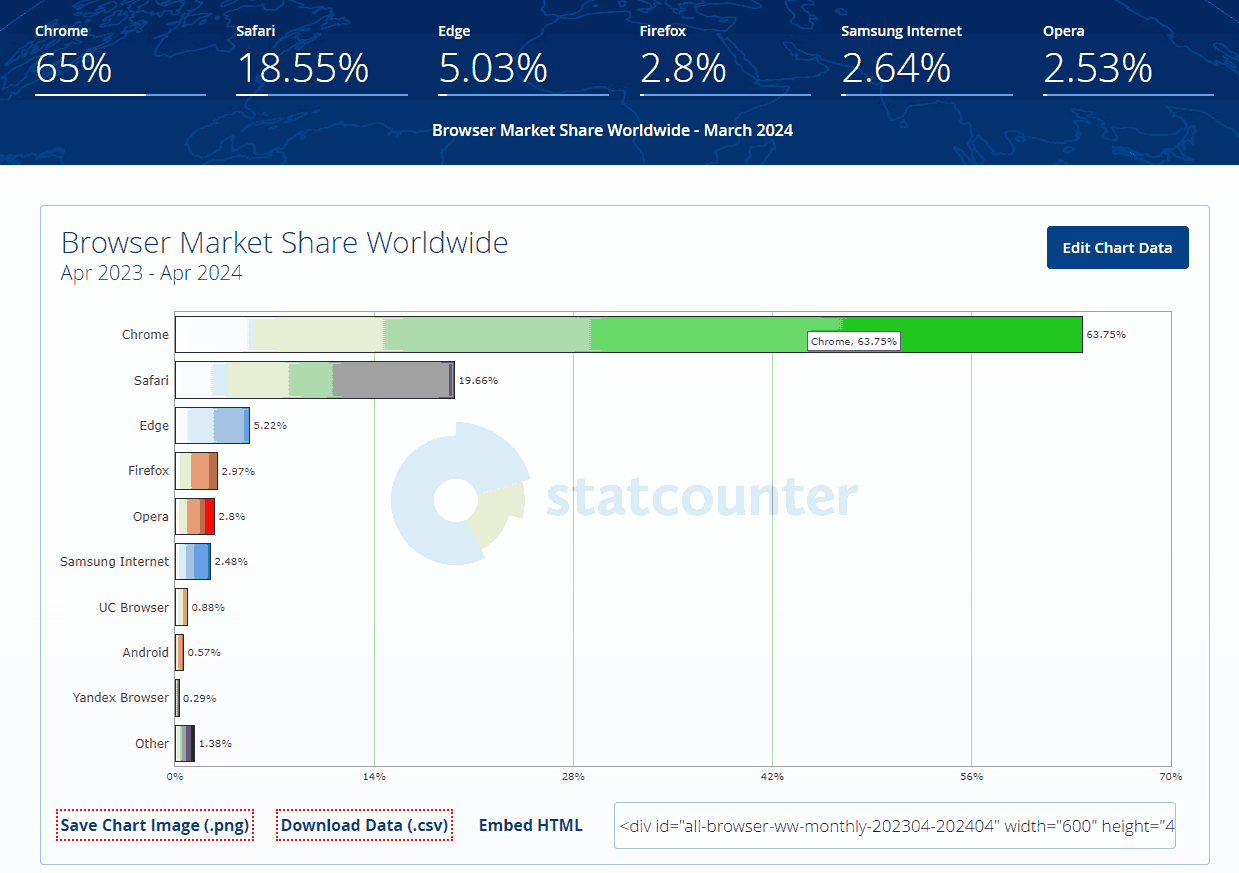
Key reasons why you should factor this in:
- Ensures complete customer satisfaction.
- Provides service across multiple platforms.
- Identifies bugs during the development process and earlier than customers.
- Avoids customer complaints.
- Ensures a competitive advantage.
Types of compatibility tests:
- Hardware.
- Operating system (OS) – such as Windows, Unix, MacOS.
- Software – e.g., ensuring that MS Word is compatible with MS Outlook.
- Network.
- Browser – for instance: Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer.
- Devices.
- Mobile – Android and iOS.
- Version – e.g. Windows 7, Windows 7 SP1.
Key terms mentioned around compatibility:
- Backward compatibility – This is where you test to see if your software is compatible with previous versions.
- Forward compatibility – This is where you test to see if your software is compatible with versions that will be coming in the future.
Steps to fit in compatibility testing in your testing approach:
- Define a set of environments or platforms the application will work on.
- Gather customer data on how your customers use your products.
- Understand the expected behavior under different configurations.
- Set up your environment and get the particular device permutations ready.
- Report any bugs that are found.
Step 2 is super important for me, and it is one where I feel more people need to build into their plans.
To gather customer data on how your customers use your products, I recommend setting up Google Analytics or an alternative statistical analysis system.
For example, when we had a website product, this data let us know what browsers and OS versions our customers used. Using this, we could tailor our test cases to ensure the product’s functionality met the user’s needs.
Another game changer with this data is that it removes bias; many a time, I have assumed that the latest device will be the most used by a user base, though when I received this data, I learned that users generally used the latest device which was from a year before.
What are the common compatibility issues found:
- Changes in the user interface (UI).
- Change in font size.
- Alignment issues.
- Change in CSS style and color.
- Scroll bar-related issues.
- Content or label overlapping.
- Broken tables or frames
While traditional compatibility testing involves manual efforts or basic automation tools like Selenium, integrating AI can enhance the process. GenAI native test agents such as like KaneAI intelligently automate testing using natural language across various environments, predicting potential compatibility issues on different devices, browsers, and operating systems.
Why Should You Use a Compatibility Testing Tool?
The biggest concern around testing compatibility is that so many test cases must be tested constantly. If we make key architectural or code changes, releasing at pace becomes nearly impossible.
So, how can you build compatibility tests into your test approach and still release at pace?
The answer to this has been to use a compatibility test tool. Now, there are lots on the market, so I recommend doing your research and picking the right tool.
Key considerations for me when selecting a compatibility tool include:
- Price.
- Usability of the tool.
- Device availability when you need to test it.
- Availability of older/newer devices and different browsers.
- The ability to incorporate the tool with your automation pack.
My recommendation is TestMu AI, primarily because:
- It supports more than 3000+ browsers and operating systems.
- It allows live interactive browser compatibility tests.
- It is cost-effective and has great customer service.
- The devices are readily available.
- Provides integration with an automation framework.
Incorporating a compatibility tool with your automation framework is a game changer, and this is a key consideration when you are at a stage where you are confident that you understand why you are testing for compatibility.
When to Perform Compatibility Testing?
Compatibility testing should be performed at various stages of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) to ensure applications function well across different platforms, software versions, and hardware. Ideal times for these tests include:
- Post-Stabilization of the Build: Once the software is stable and less likely to change, initiating compatibility tests can be more effective.
- After Updates or Changes:.
- To the operating system (OS) the application uses.
- When browser updates might affect the application.
- If the application begins interacting with new hardware.
- Following updates to third-party software and libraries used by the application.
Integrating compatibility tests throughout the SDLC is crucial, as issues can arise at any stage, making ongoing testing necessary to identify and resolve potential incompatibilities.
How to Perform Compatibility Testing?
To perform a compatibility test effectively, follow these steps:
- Understand Target Platforms: Identify operating systems, browsers, hardware configurations, and versions of third-party software relevant to the application.
- Create test cases: Prepare detailed test cases for every platform and scenario it might be going through.
- Set up test environment: Set up a test environment to mimic end-user installations, including OS, devices, browsers, and third-party software.
- Execute Tests: In every test case executed, follow the steps exactly as outlined; record the results and analyze the encountered problems or bugs for each target platform.
- Run Retests: Verify the fixes by retesting the application to ensure no new error was introduced with the fixed issues before moving to production.
Retesting is a crucial step as it helps to ensure that the particular error in the applications or websites is resolved without giving rise to any further errors or bugs. You can repeat the testing process until all the test cases are resolved. This validation should be done before moving it to real production.
Common Compatibility Testing Defects
Compatibility test identifies defects across different environments. Key issues include:
- UI Changes: Variations in screen resolution, aspect ratios, and font rendering.
- Alignment and Overlapping: Misalignment and content overlap due to differing screen sizes.
- Dropdown Menus: Failures, particularly on various OS or touch devices.
- CSS Issues: Inconsistencies in style and color rendering across browsers.
- Scroll Bar Problems: Malfunctioning scroll bars and unusual scrolling behaviors.
- Pop-up Windows: Diverse behaviors or blocks on different platforms.
- Media Playback: Discrepancies in video and audio capabilities across devices.
- Tables and Frames: Broken or improperly displayed tables and frames. Effective testing can pinpoint and rectify these issues, enhancing platform consistency.
Types of Compatibility Testing
There are two types of compatibility tests. Here is a quick breakdown.

Forward Compatibility Testing
Forward compatibility test, or upward compatibility test, ensures that a current software version remains functional with future versions of related components like operating systems, browsers, and third-party libraries. This type of testing is crucial for maintaining stability and user experience during system upgrades.
For example, the latest version of the software application undergoes the following forward compatibility test.
Windows Vista → Windows XP → Windows 7 → Windows 8 → Windows 8.1 → Windows 10 → Windows 11
Backward Compatibility Testing
A backward compatibility test ensures that new software versions maintain compatibility with older components, preventing issues during upgrades. This is vital for users and businesses reliant on legacy versions for specific needs.
For example, the old version of the software application undergoes the following backward compatibility test.
Windows 11 → Windows 10 →Windows 8.1 → Windows 8 → Windows 7 → Windows Vista → Windows XP
Further forward and backward compatibility test has various sub-categories discussed below:
- Validates software performance across different hardware setups, like graphics cards and processors, to prevent functional issues.
- Assesses software performance over various network types (e.g., Wi-Fi, 4G) to ensure no connectivity, security, or performance issues.
- Checks software behavior across operating systems (OS) like Windows, macOS, and Linux to avoid compatibility problems.
- Evaluates software on multiple devices (laptops, tablets, phones) to ensure consistent functionality across different hardware.
- Focuses on software operation on mobile devices, selecting test devices based on market trends to cover a broad user base.
- Ensures web applications display and function consistently across various browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, and Safari, regardless of browser version.
- Verifies that applications function well with other software or third-party tools, such as opening PDFs in Adobe Acrobat or displaying content in Microsoft Excel.
- Check that updates or new software releases refrain from introducing issues with older versions, especially concerning databases, APIs, user interfaces, and file formats.
Compatibility Test Tools
Compatibility testing ensures software consistency across various systems and environments. This guide explores tools for developers and QA professionals to detect and resolve issues effectively, enhancing application robustness and user satisfaction.
1. TestMu AI
It is an AI-native test orchestration and execution platform that lets you run manual and automated testing at scale on the cloud with over 3000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations.
- TestMu AI Real-Time Testing: TestMu AI has established itself as a premier choice for thorough testing compatibility, serving as an effective live interactive web browser compatibility testing tool. With 3000+ environments of browsers (Chrome, Chrome, Safari, Opera, Yandex, IE, Yandex) and operating systems (Windows, MacOS), users can quickly identify compatibility issues across multiple environments.
- TestMu AI Real Device Testing: As a leader in device compatibility testing, TestMu AI provides access to an extensive selection of 3000+ environments of latest to legacy real mobile devices for precise testing on smartphones and tablets such as iPhone, Samsung Galaxy, Pixel, and more. This ensures consistent application behavior across different screen sizes and resolutions, enhancing the user experience across diverse devices.

Additionally, when a Live session starts, you can easily access various features from the toolbar:
- Parallel Testing: TestMu AI enables simultaneous testing across various browsers and devices, boosting efficiency.
- Screenshots Testing: Quickly capture screenshots to ensure responsiveness and identify visual issues.
- Responsive Testing: Validate your application’s responsiveness across diverse mobile devices for a consistent user experience.
- Local Testing: Effortlessly tests locally hosted apps, websites, and web apps.
- Geolocation Testing: Test your application’s behavior based on different geolocations to ensure accurate functionality across regions.
- Accessibility Testing: Ensure your application meets accessibility standards for all users.
2. Browsera
It is a web-based tool to test websites for scripting and layout issues. It crawls over your website and creates a report that finds compatibility issues on various browsers. Using Browsera, it is possible to take screenshots of your website in different browsers. Through this, you can quickly identify and resolve the issues.
3. GhostLab
It is a tool that simultaneously performs compatibility tests for your website across all devices. You can sync the website across all devices to check its function on different platforms. Both manual and automation testing can be done using GhostLab and give detailed reports on compatibility issues.
Compatibility Testing on the Cloud
Running compatibility tests on cloud-based platforms lets you test on a wide range of browsers, devices, and operating systems. Such access can be difficult in a local in-house environment. To overcome this, a cloud-based platform can test applications simultaneously across multiple browsers, lowering the efforts and time required for testing.
AI-native test orchestration and execution platforms like TestMu AI enable you to perform manual and automated compatibility testing on 3000+ browsers, mobile devices, and OS. With the TestMu AI platform, you can quickly test your website and mobile application in real user environments by leveraging its real device cloud .
It also offers other features, like parallel testing , visual regression testing, and debugging tools, to simplify identifying and fixing compatibility issues.
Subscribe to our TestMu AI YouTube Channel for the latest updates on tutorials around Selenium testing, Cypress testing , and more.
Manual Compatibility Testing Using TestMu AI
Suppose you want to test websites on a desktop using TestMu AI. To do this, here are the following steps:
- Sign up for free and log into your TestMu AI account.
- From the user Dashboard, click Real > Desktop.
- Enter your web URL and select the test configuration per your choices, like browser, version, OS, and resolution. Then click Start.
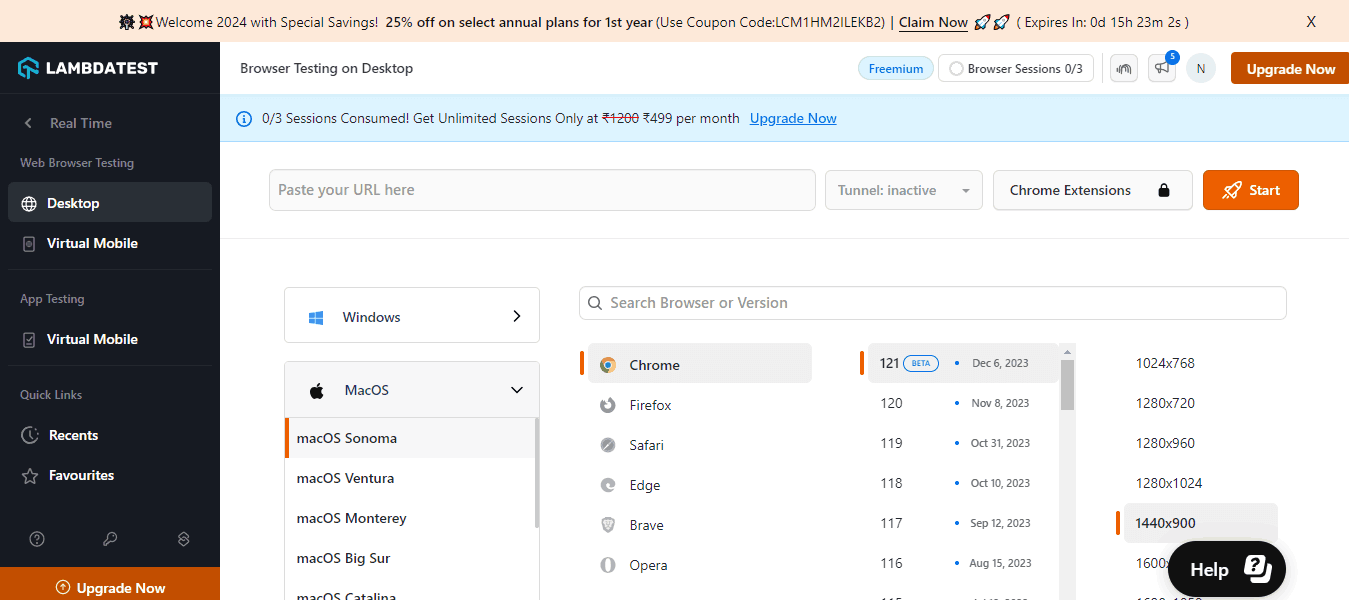
It will allocate you a cloud-based machine running real OS and browsers, and now you can perform your manual compatibility tests.

Automated Compatibility Testing Using TestMu AI
Automation testing with TestMu AI streamlines compatibility checks across various devices and browsers. It allows you to execute automated tests swiftly on multiple real browsers and devices, significantly reducing testing time and effort.
TestMu AI is compatible with leading automation testing frameworks such as Selenium, Playwright, Cypress, Appium, and more. These frameworks facilitate the creation and execution of test scripts efficiently.
To enhance your compatibility tests and minimize testing efforts, follow these steps to conduct automated web tests on TestMu AI:
- Log into your TestMu AI account and navigate to Automation from the left panel.
- Select any from the Demo Project or Configure Test Suite.
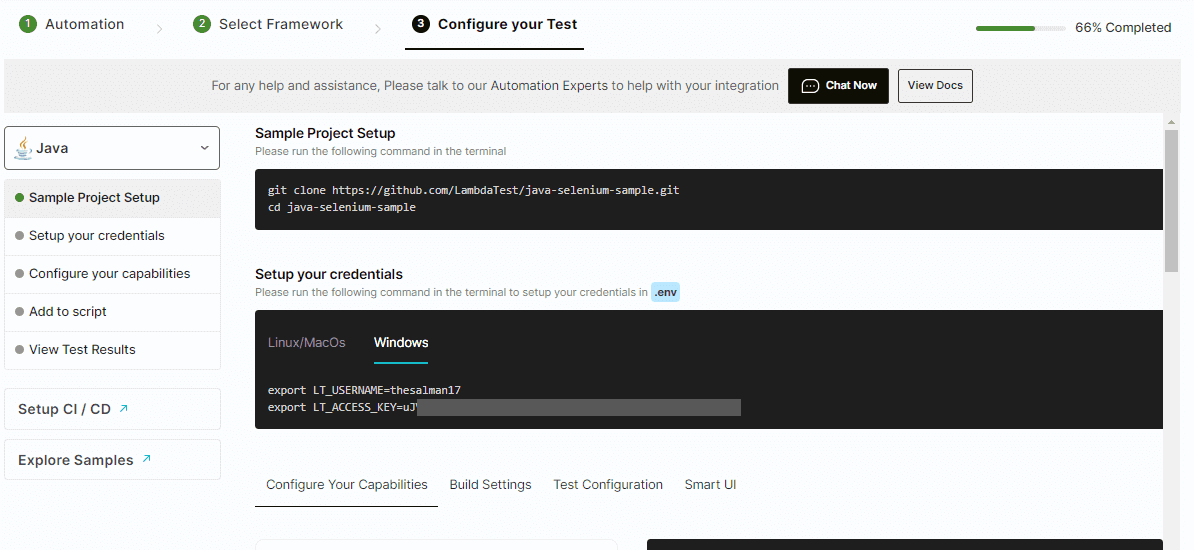
- To run the automated test, choose Configure Test Suite and select your preferred automation framework.
- Follow the screen instructions to configure the test.
Note: Run online compatibility tests across 3000+ real browsers and OS. Try TestMu AI Today!
Who is Involved in Compatibility Testing?
Here are the key individuals responsible for performing compatibility tests in software testing:
- QA Engineers: Primarily responsible for designing, executing, and analyzing test cases across different hardware, software, and platforms.
- Developers: Collaborate with QA to identify and fix compatibility issues.
- Product Managers: Define compatibility requirements and prioritize testing efforts.
- End-users: Can provide valuable feedback on real-world compatibility issues.
Benefits of Compatibility Testing
It offers several benefits that enhance the software development process:
- Simplifies the SDLC: It identifies defects early in the development cycle, facilitating timely bug fixes and preventing complications that arise from cross-platform discrepancies.
- Early Bug Detection: Testing across various platforms allows early identification of issues, giving developers adequate time to address them before they impact the development timeline or product quality.
- Quality Assurance: Ensures usability, reliability, and stability across different devices, browsers, and operating systems, leading to a smoother and more successful software release.
- Enhanced Security: Helps uncover and mitigate security vulnerabilities, ensuring that software operates securely across all intended environments.
Challenges of Compatibility Testing
Specific challenges can arise when performing compatibility tests in a local or a cloud environment. It is crucial to address those while testing to get reliable test results. Let us learn a few of those challenges:
- Device Fragmentation: Numerous devices, browsers, and operating systems make it challenging to ensure consistent application functionality across all platforms.
- Setup Costs: Establishing diverse test environments is expensive and time-consuming.
- Evolving Technologies: Continuous updates in software technology mean applications might not function correctly on new devices or operating systems.
- Cross-Cultural Challenges: International applications need to support multiple languages, time zones, and date formats, adding complexity and costs to testing.
Best Practices for Compatibility Testing
To ensure reliable results and high-quality applications, here are streamlined best practices for testing compatibility:
- Test Early and Often: Begin compatibility tests early in the Software Development Life Cycle and conduct it frequently to catch and resolve issues promptly, saving time later.
- Test on Real Devices: Use actual devices to accurately assess how the application functions on specific hardware and operating systems, allowing for timely corrections before release.
- Prioritize Critical Issues: Focus tests on essential functions and features to effectively allocate resources and ensure key aspects of the application perform well across all platforms.
- Test in Various Environments: Execute tests across different network conditions, including slow or unstable networks, to confirm application consistency in all expected settings.
- Collaborate With Developers: Maintain close communication between testers and developers to quickly identify and solve compatibility issues, ensuring the application meets all design and functionality standards.
Example of Compatibility Testing
Consider a web application initially designed for Windows OS desktops. To ensure it meets user requirements across different environments, the application is tested on various Windows versions like Windows XP (through a Test on Windows XP Simulator), Windows 8, 10, and 11. Additionally, it’s evaluated on different devices, including laptops, mobiles, and tablets, to verify consistent functionality
The testing extends to assessing the application’s performance on popular web browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge, ensuring it operates smoothly regardless of the browser used.
Is Compatibility Testing Akin to Cross Browser/Device Testing?
Cross-browser and compatibility testing may seem identical. However, in reality, there are differences which are worth considering.
It is a broader category, covering tests on diverse operating systems, screen resolutions, browsers, devices, and network conditions. In simple terms, these tests address hardware, operating systems, and devices.
On the other hand, cross-browser testing is a subset of compatibility tests that tests software performance across various web browsers, such as Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc. This includes testing on different versions of the same browser and distinct browsers.
Cross-device testing is a subset of compatibility tests that focuses explicitly on testing mobile apps across different devices supported by platforms like Android and iOS.
Conclusion
Testing compatibility is crucial in this current time, where technology is evolving faster. It is an essential process that ensures software applications can work seamlessly across multiple platforms, browsers, devices, and environments. In this tutorial, the process outlined for performing a compatibility test can help you get started.
Following the best practice, you can detect and resolve any compatibility issue early in development. This can save you time and effort. You should prioritize compatibility tests to ensure software applications and websites meet users’ expectations.
My closing statement is that if you do not have compatibility testing built into your testing approach, it can be a game changer for your users, and I recommend that you add it as soon as possible!
2M+ Devs and QAs rely on TestMu AI
Deliver immersive digital experiences with Next-Generation Mobile Apps and Cross Browser Testing Cloud
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests




